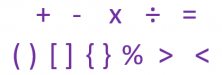
Symbols are images that represent something. In general, symbols are determined by their context. In mathematics, symbols generally represent operations or relationships between numbers or values.
In this week’s post we’re going to talk about mathematical symbols. There are a lot, so we’re just going to look at the most important.
Addition
+
This is the symbol of addition. It represents the addition of one number to another.
Example: 5 + 4. We have 5 units and we add 4.
Subtraction
–
This is the subtraction symbol. It represents the subtraction of one number from another.
Example: 6 – 3. We have 6 units and we take away 3.
We also use it to write a negative number.
Example: -5
Multiplication
×
The symbolises multiplication. It represents the number of times that you need to add a number.
Example: 3 × 4 = 3 + 3 + 3 + 3
There are some other symbols we can also use to represent multiplication:
A dot 3 · 4
An asterisk 3 * 4
Division
÷
This is the division symbol. It represents the total number of times you need to share equally.
Example: 24 ÷ 6. We need to share 24 units into 6 equal parts.
To represent division, we can also use some other symbols:
Two dots 24 : 6
A slash: 24 / 6
Equals
=
This is the equals symbol. It represents the equilibrium between two expressions and is one of the most important symbols in mathematics.
Example: 5 + 6 = 11. Both the expression on the right and on the left are equal.
Brackets: parentheses, square, and curly
( ) , [ ] , { }
Parentheses, square, and curly brackets are used to group operations when several appear in the same expression and we want to specify the order in which to solve them.
Example: 10 ÷ ( 5 – 3 ). In this case, the first operation that we need to resolve is the one that’s inside the parentheses, or brackets. Once we’ve done this, we can solve the divison.
Percentage
%
This symbol represents percentage. It represents the given amount as a part of a total of 100.
Example: 26%. There 26 units of a total of 100.
Greater than and Less than
> , <
These are the greater than and less then symbols. We use them to compare quantities.
Example: 6 > 2. In this case we can see that 6 is greater than 2
Example: 9 < 15. In this case the symbol is indicating that 9 is less than 15.
I hope you’ve enjoyed this week’s post. Have you used these mathematical symbols? Do you know any more? If you do, leave a comment below so that everybody can learn them.
You can practice all this and more with Smartick. Register and try it free!
Learn More:
- Greater Than and Less Than Symbols
- Learn How to Perform Combined Operations
- Math Symbols: Greater Than, Less Than, and Equal
- Singapore Bar Model and Percentages
- How to Apply the Order of Operations








You did not include the long division symbol.