Homeschooling, once considered an alternative education method, has rapidly gained popularity in the United States, becoming a mainstream approach to education. With an estimated 3.1 million homeschool students in grades K-12 in the 2021-2022 academic year, homeschooling is emerging as one of the fastest-growing forms of education in the country.
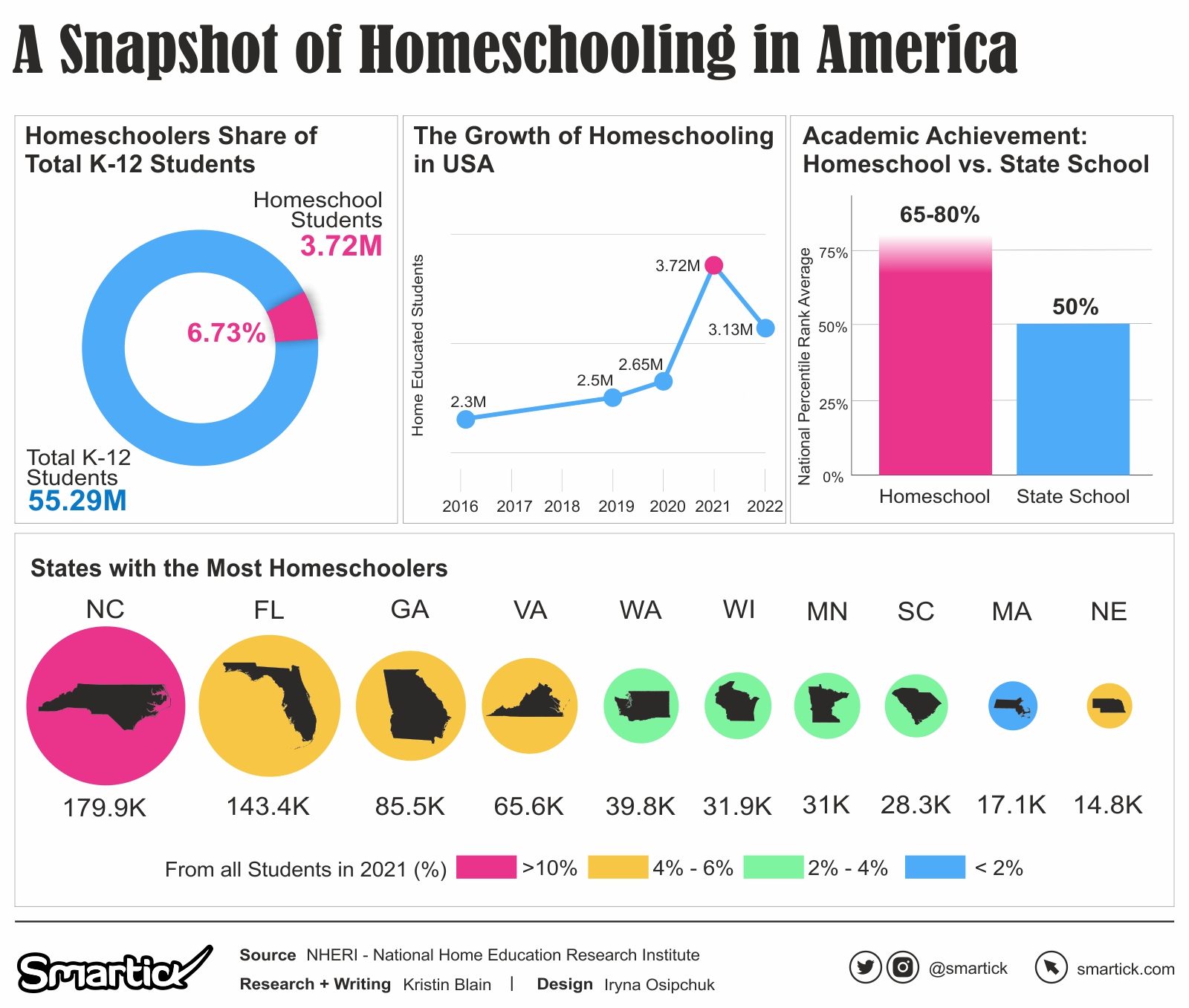
Our visualization explores NHERI’s key research findings, statistics, and trends related to homeschooling, shedding light on its diverse demographics, academic performance, social and emotional development, and long-term success.
General Facts, Statistics, and Trends
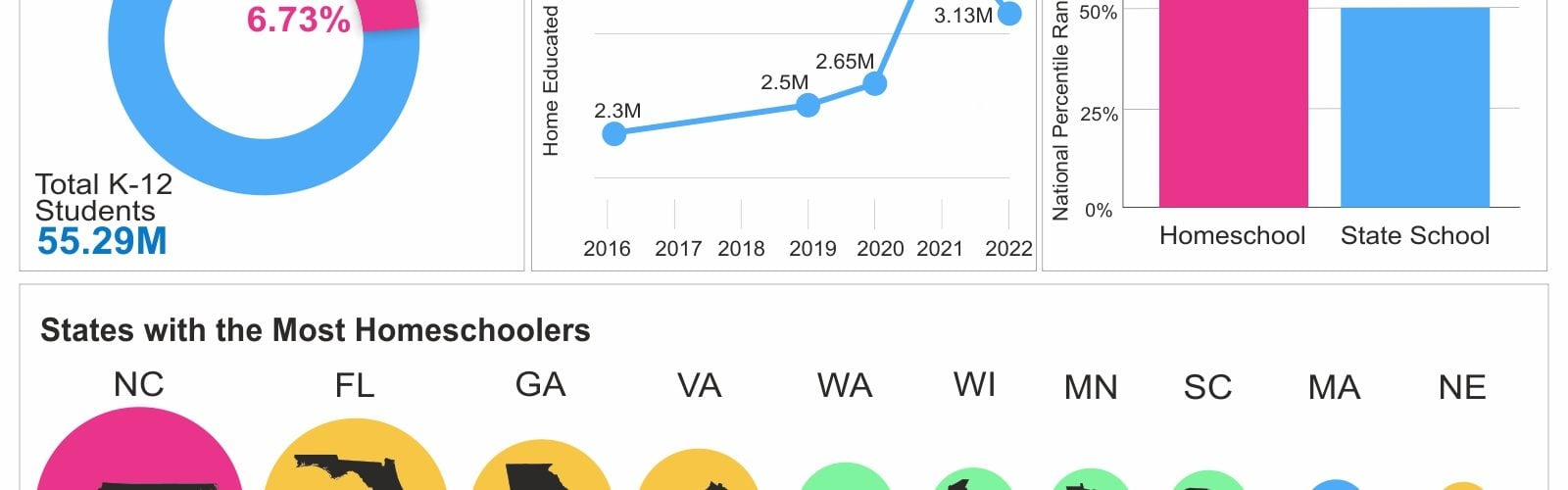
In the United States, approximately 3.1 million students were homeschooled in the 2021-2022 academic year, representing around 6% of school-age children.
Homeschooling has been growing at an estimated rate of 2% to 8% per year, but the growth rate spiked significantly from 2019-2020 to 2020-2021.
Homeschooling is not limited to any specific demographic; it encompasses a wide range of families, including atheists, Christians, conservatives, liberals, low-income, middle-income, and high-income families.
Taxpayers save over $56 billion annually due to the homeschooling population, as homeschool families bear the financial responsibility of their children’s education.
Reasons and Motivations for Home Educating
- Parents and youth choose homeschooling for multiple reasons, such as customizing the curriculum for each child, achieving higher academic outcomes, employing alternative teaching approaches, fostering stronger family relationships, providing a safer environment, and instilling specific values and beliefs.
- Homeschooling can also serve as an alternative education option during crises or when parents aim to shield their children from racism or low expectations in conventional schools.
Homeschoolers’ Academic Performance
- Home-educated students typically score 15 to 25 percentile points higher than their public school counterparts on standardized academic achievement tests.
- A significant number of peer-reviewed studies demonstrate that homeschool students consistently outperform their institutional school peers.
- Homeschool students’ academic success remains unaffected by their parents’ level of formal education or family income.
Homeschool students perform above average on college admission tests like the SAT and ACT, making them sought-after candidates for colleges and universities.
Social, Emotional, and Psychological Development
- Research indicates that homeschool students excel in social, emotional, and psychological development, surpassing their conventionally schooled peers.
- Homeschool students actively engage in various social and educational activities beyond their homes, participating in field trips, community service, sports teams, and other community-based endeavors.
- Evidence suggests that homeschool students experience less harm and are more politically tolerant than public-schooled students.
Gender Differences in Children and Youth
- Homeschooling provides a unique opportunity for young people to explore their identity, resulting in the development of a strong sense of self, particularly among girls.
- Boys often find their energetic nature and physical expression more accommodated in home-based education compared to traditional schools.
Success in the “Real World” of Adulthood
- Studies indicate that adults who were homeschooled fare well in various aspects of adult life, including higher rates of community service engagement, political involvement, college attendance, and internalization of their parents’ values and beliefs.
- Research consistently demonstrates that adults who were homeschooled succeed and perform better than those who attended institutional schools.
Homeschooling in America has experienced substantial growth and proven to be a successful educational option across various demographics. Homeschool students consistently achieve higher academic results, develop robust social and emotional skills, and excel in adulthood.
As the homeschooling movement continues to evolve, it is essential for policymakers, educators, and parents to collaborate and ensure the provision of resources, support networks, and opportunities for socialization. By recognizing the diverse motivations and benefits of homeschooling, society can foster an inclusive educational landscape that empowers families to choose the best path for their children’s education.