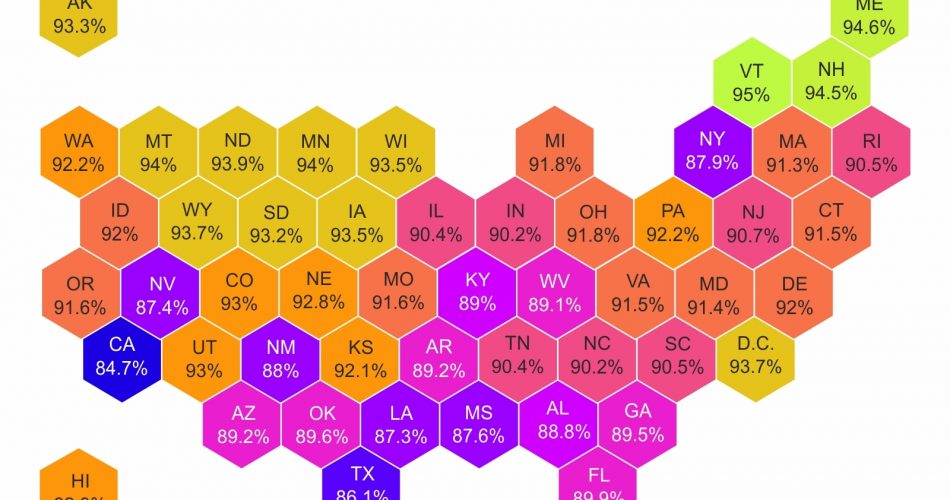
At the forefront of states with the highest percentage of high school dropouts are California, Texas, and New York. California, despite being the most populous state, faces a significant educational hurdle with only 84.7% of residents aged 25 and over holding a high school diploma or higher. Following closely are Texas, with 86.1%, and Louisiana, with 87.3%.
Delving deeper into the data, Nevada, Mississippi, New York, New Mexico, Alabama, Kentucky, and West Virginia also find themselves among the bottom 10 states with high school dropout rates. These figures underscore the challenges these states face in ensuring educational success and opportunities for their residents.
On the flip side, states such as Vermont lead the pack in educational attainment, boasting a remarkable 95% of residents aged 25 and over holding high school diplomas or higher. Maine and New Hampshire closely follow, with 94.6% and 94.5% respectively. Montana and Minnesota round out the top five, with both states reporting a 94% high school graduation rate.
These disparities highlight the complex interplay of socioeconomic factors, educational policies, and community support systems that influence high school dropout rates. Efforts to address these disparities require targeted interventions tailored to each state’s unique needs, focusing on improving educational opportunities, providing support to at-risk students, and fostering a culture of academic success.
As policymakers and educators continue to grapple with the challenge of reducing high school dropout rates, it is essential to draw lessons from both the successes and struggles of different states. By working collaboratively and implementing evidence-based strategies, we can strive towards a future where every student has the opportunity to succeed and fulfill their potential, regardless of their zip code.